Understanding the Basics of Electronics: A Beginner’s Guide ⚡
Electronics is all around us. From the devices we use every day to the systems that power our homes, electronics make our modern world function. Whether you’re designing a simple circuit or working on advanced projects like robotics, understanding the fundamentals of electronics is key to success in the field. In this guide, we’ll cover the essential components, concepts, and tools you need to get started.
The Core Components of Electronics 🔌
To build a functioning electronic device, you’ll need to understand a few basic components. Let’s take a look at the most common ones:
- Resistors: Resistors are components that limit or resist the flow of electric current. They are essential in protecting delicate parts of a circuit from receiving too much current. Resistors are measured in Ohms (Ω).
- Capacitors: These components store and release electrical energy. They’re used in power supplies to smooth out voltage or to filter signals. Capacitors are measured in Farads (F).
- Diodes: A diode allows current to flow only in one direction. This makes them useful in circuits where you need to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), like in power supplies.
- Transistors: Transistors are crucial for amplifying or switching signals. They act as gatekeepers in circuits, controlling how much current flows through a particular part of the circuit. They can also be used in digital circuits to build logic gates.

How Does an Electronic Circuit Work? 🧠
At its simplest, an electronic circuit is a closed loop of wire and components that allows the flow of electric current. The current is driven by a power source, such as a battery or a power supply. The current flows through various components—like resistors, capacitors, and transistors—each of which performs a specific task.
Two types of current can flow in a circuit:
- Direct Current (DC): This current flows in one direction. It’s used in most battery-powered devices, like your mobile phone or flashlight.
- Alternating Current (AC): This current alternates direction periodically. AC is used for power transmission over long distances, like the electricity that powers homes and businesses.
Ohm’s Law: A Key Principle 🧑🔬
One of the most important principles in electronics is Ohm’s Law. It states that the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) is: V=I×RV = I \times R
Where:
- V is voltage (measured in volts)
- I is current (measured in amperes)
- R is resistance (measured in ohms)
Understanding this relationship is crucial when designing circuits. For example, if you know the voltage supplied to a circuit and the resistance of the components, you can calculate how much current will flow.
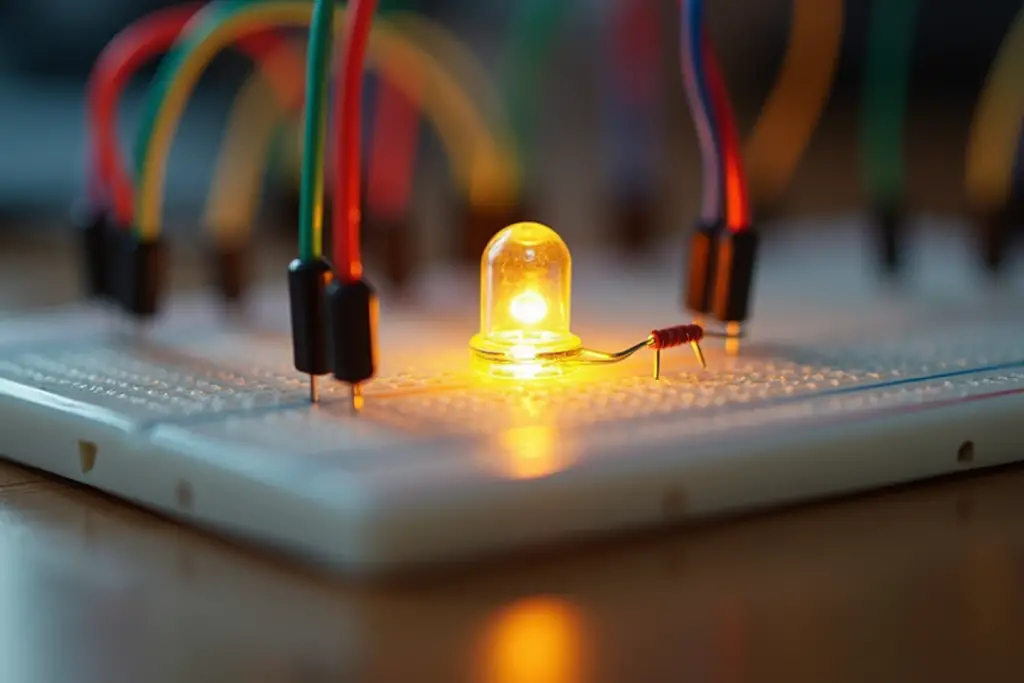
Building Your First Circuit 🔧
One of the best ways to learn about electronics is to build simple circuits. A classic beginner circuit is the LED circuit, where you connect an LED and a resistor to a power source.
Components You’ll Need:
- LED (Light Emitting Diode): This will light up when current flows through it.
- Resistor: Limits the current flowing to the LED, preventing it from burning out.
- Power Source: A battery or power supply.
- Breadboard: A platform for assembling your circuit without soldering.
Steps:
- Connect the resistor: Place one end of the resistor in the breadboard.
- Connect the LED: Place the LED so that it connects to the resistor.
- Power the circuit: Connect the positive terminal of the battery to one side of the circuit, and the negative terminal to the other.
- Test it: If everything is connected correctly, the LED should light up!
Tools You’ll Need 🧰
As you progress in your electronics journey, you’ll need some basic tools to test and troubleshoot your circuits:
- Multimeter: Measures voltage, current, and resistance. This tool is essential for diagnosing problems in your circuits.
- Oscilloscope: Visualizes electrical signals, allowing you to see how the current behaves in your circuits.
- Soldering Iron: Used for joining components permanently onto a circuit board.

Safety Tips for Electronics ⚠️
Working with electronics can be fun and rewarding, but safety is always a priority. Here are some important tips:
- Always Disconnect Power: Before making changes to a circuit, always disconnect the power source to avoid accidents.
- Check for Short Circuits: A short circuit can cause components to overheat and fail. Use a multimeter to test your circuit before powering it up.
- Use Insulated Tools: Make sure to use tools with proper insulation to reduce the risk of electric shock.
- Work in a Ventilated Area: When soldering, work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes from the solder.

Conclusion 🎓
Electronics is an exciting and versatile field with endless possibilities. Whether you’re designing simple gadgets or working on complex projects, having a solid understanding of the basic principles will set you up for success. Start with simple projects, experiment, and always keep learning. With time, you’ll develop the skills needed to create and troubleshoot circuits of all kinds.
Table: Common Electronic Components and Their Functions
| Component | Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | Limits current flow | LED circuits, voltage dividers |
| Capacitor | Stores and releases energy | Power supply filtering, timing circuits |
| Diode | Allows current in one direction only | Rectifiers, protection circuits |
| Transistor | Amplifies or switches electrical signals | Amplifiers, logic gates |
| Inductor | Resists changes in current | Filters, power supplies |
Now that you’ve got a grasp of the basics, it’s time to dive in and start building your own circuits. Happy experimenting! 🎉

